Top Interpersonal Skills (Examples & How to Improve)
Trust Score: 4.7
361 reviews

Table of Contents
"Strong interpersonal skills matter in school, work, and everyday life, discover how to improve yours."
When it comes to career growth, technical expertise may get your foot in the door, but it’s your interpersonal skills that truly set you apart. Employers today want professionals who can not only perform tasks but also communicate effectively, work in teams, and build positive relationships.
That’s why showcasing the right abilities on your resume is so important. Start by identifying the most impactful skills to put on your resume, a mix of both hard and soft skills that prove you can deliver results while collaborating with others. If you’re just beginning your career, choosing the right skills for a fresher’s resume can make all the difference in how recruiters view your potential.
Of course, balance matters. Filling your application with endless buzzwords won’t impress anyone. Instead, focus on quality by understanding how many skills to include on a resume to keep it concise yet powerful. A well-structured resume with the right skills highlighted shows employers that you know what’s relevant and valuable to their organization.
At the heart of it all, interpersonal skills remain your hidden strength whether you’re leading a project, solving a conflict, or simply collaborating with your team. They might not always appear in job descriptions, but they’re often the deciding factor in who stands out during the hiring process.
What are Interpersonal skills?
Interpersonal skills are the abilities we use to interact and communicate effectively with others. They go beyond words, encompassing everything from how we listen and express ourselves to how we handle emotions and resolve conflicts. These skills are also considered people management skills, as they are the building blocks of human connection, skills that help us build relationships, navigate conversations, and create understanding.
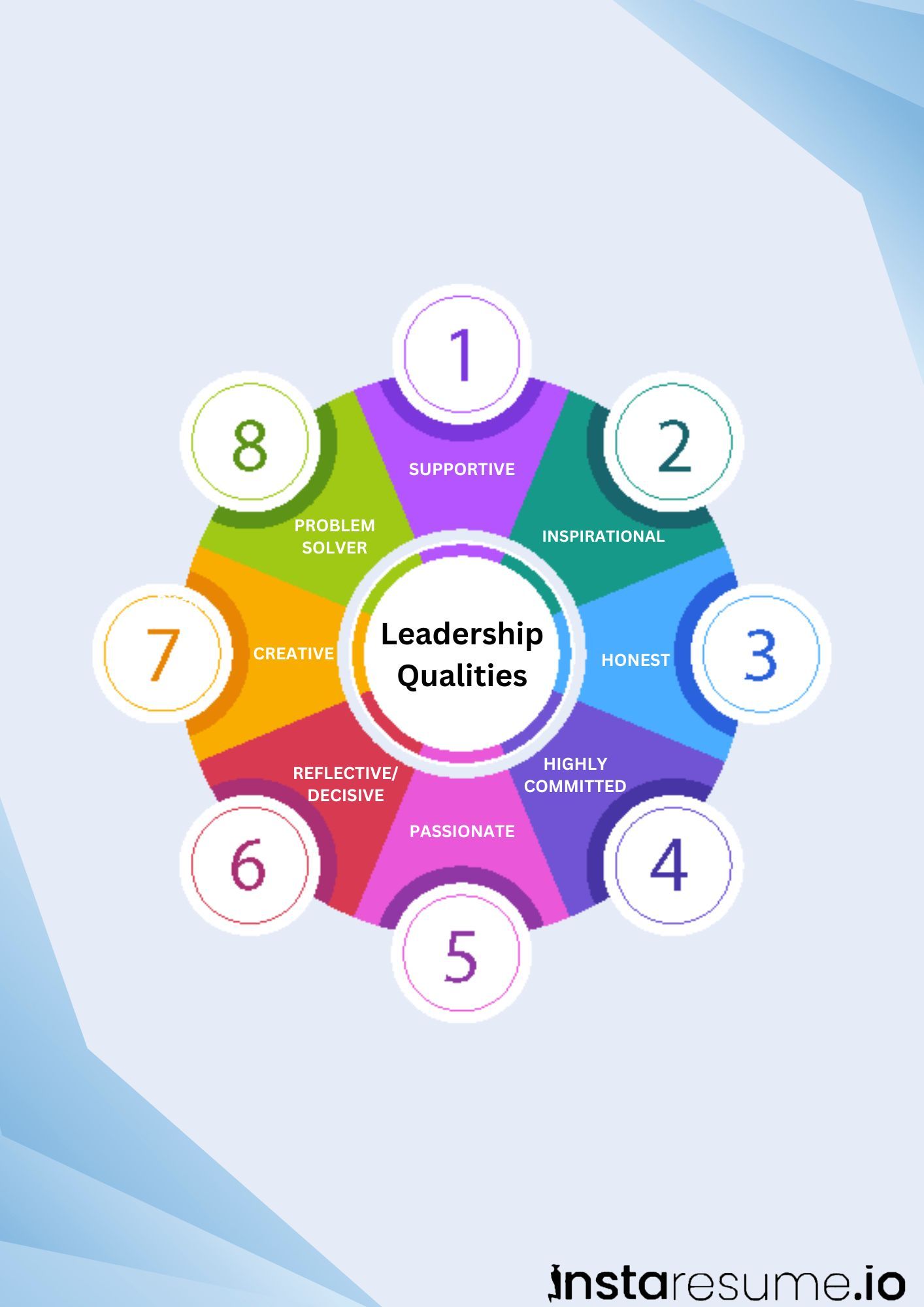
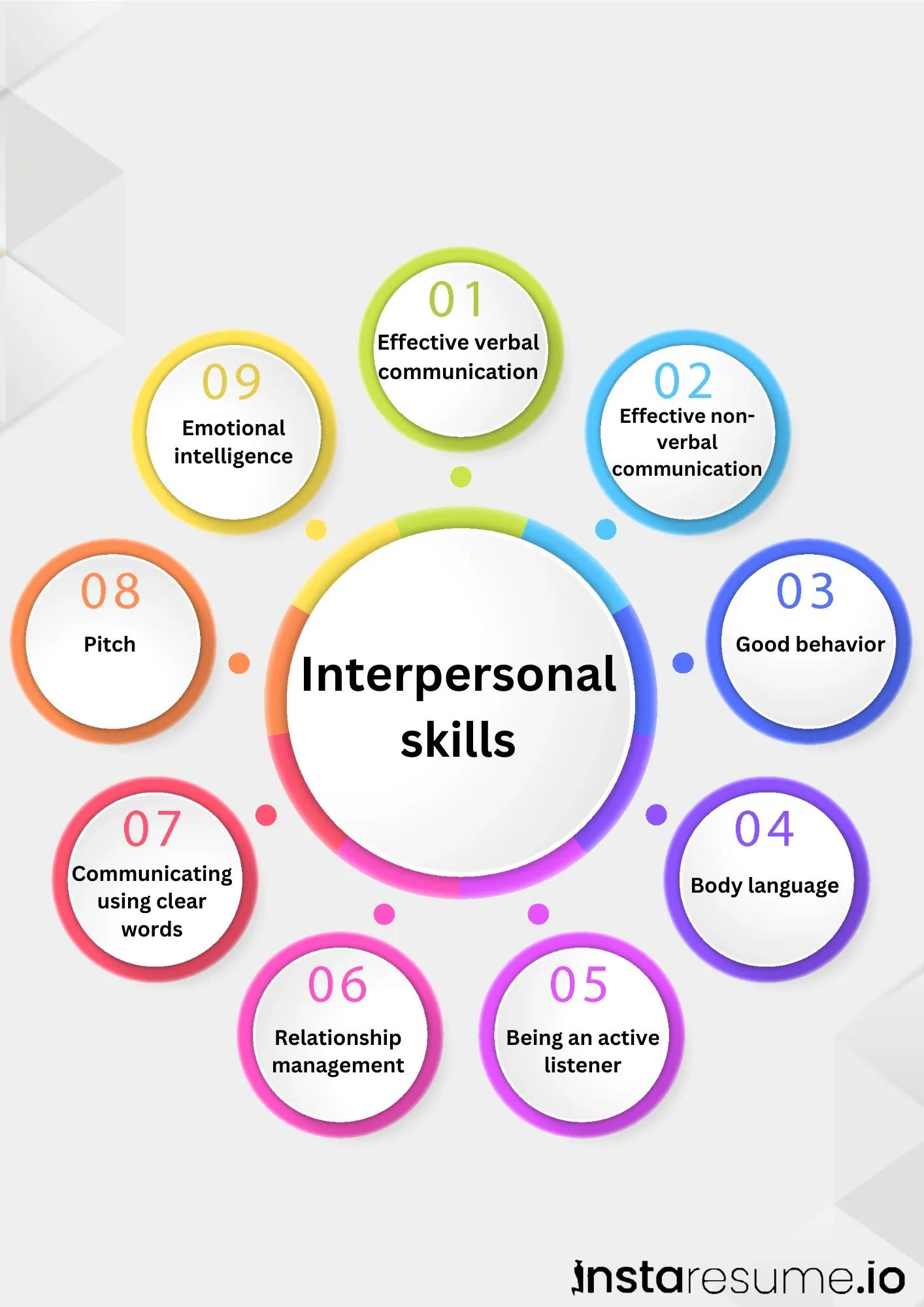
1. Communication
This skill goes beyond just talking—it’s about expressing your thoughts and ideas in a clear, concise way while also being an active listener. Good communication means choosing the right words, tone, and body language to connect with others, as well as truly understanding what the other person is saying.
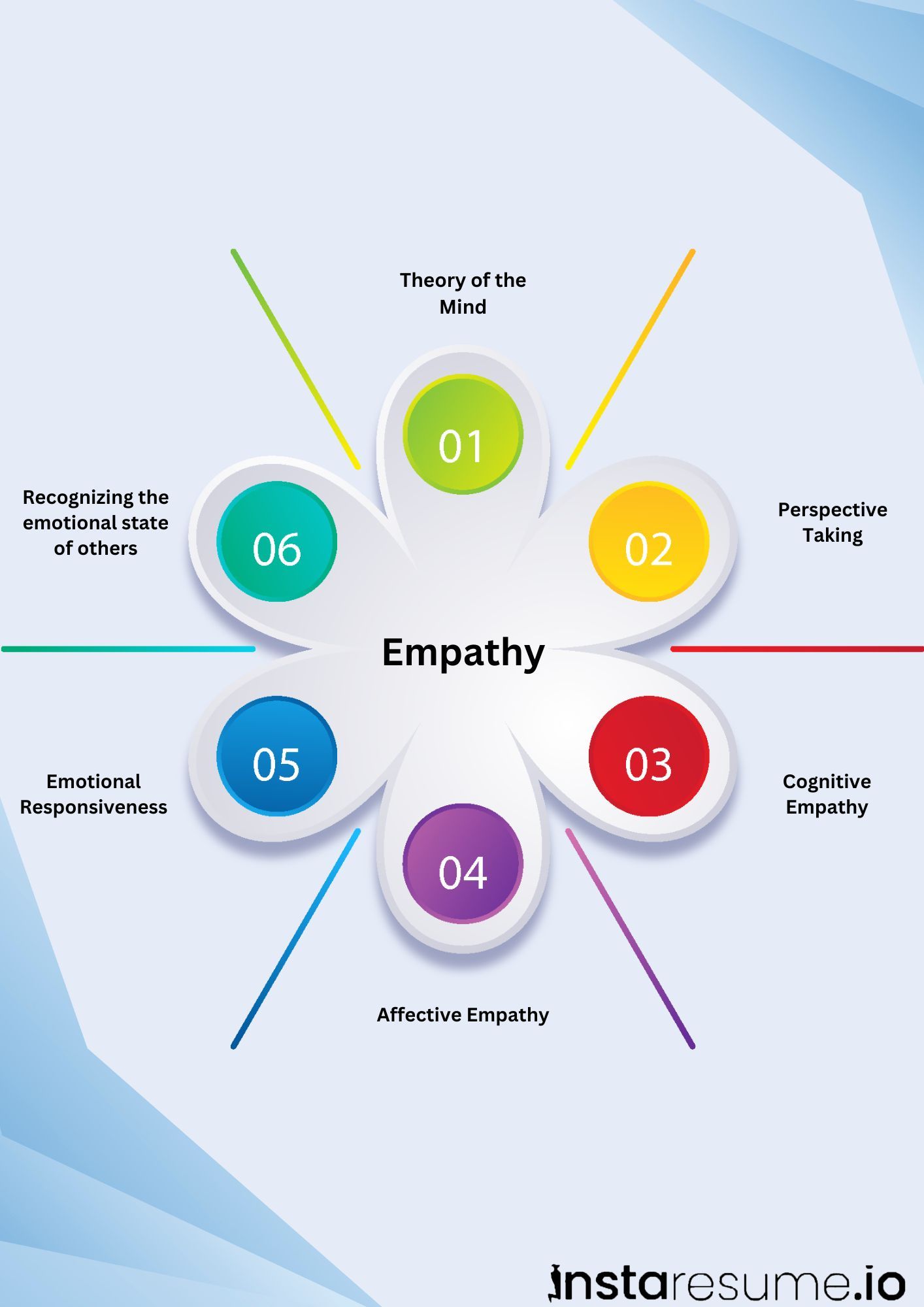
2. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to put yourself in someone else’s shoes and understand their emotions, perspectives, and needs. It helps in building trust, showing compassion, and strengthening relationships both personally and professionally.
3. Teamwork
Working in a team requires cooperation, sharing responsibilities, and supporting one another to achieve a shared goal. Strong teamwork skills involve respecting others’ opinions, balancing individual and group priorities, and creating an environment where everyone feels valued.
4. Conflict Resolution
Disagreements are natural, but resolving them constructively is key. Conflict resolution means addressing issues calmly, listening to all sides, finding common ground, and ensuring that differences don’t harm relationships or productivity.
5. Adaptability
Every situation and person is different, and adaptability is about being flexible enough to adjust to changing circumstances. Whether it’s learning a new skill, working with different personalities, or handling unexpected challenges, adaptability keeps you effective in dynamic environments.
6. Patience
Patience helps you stay calm and composed when dealing with delays, mistakes, or difficult people. It prevents frustration, improves decision-making, and makes interactions more positive and respectful.
7. Leadership
Leadership isn’t only about being in charge—it’s about motivating, guiding, and empowering others. A good leader communicates vision clearly, sets an example, supports their team, and helps people grow while driving progress toward goals.
8. Positive Attitude
Maintaining a positive outlook makes collaboration smoother and interactions more pleasant. Enthusiasm, optimism, and resilience encourage others, build morale, and create a more productive and friendly environment.
The role of interpersonal skills at work
In the workplace, interpersonal skills are everything. They influence how we collaborate, solve problems, and maintain harmony in teams. Whether you’re managing a team, working alongside peers, or interacting with clients, strong people skills can set you apart.
Here’s why they’re in such high demand:
Effective communication: Misunderstandings can lead to missed deadlines, mistakes, or conflicts. Strong communicators prevent that by fostering clarity and openness.
Building relationships: Success often hinges on your ability to connect with colleagues, clients, or stakeholders. Trust and rapport are essential for collaboration and growth.
Problem-solving: When conflicts or challenges arise, interpersonal skills ensure issues are addressed constructively rather than escalating.
Adaptation in team dynamics: As workplaces evolve, teams often consist of diverse individuals. Good interpersonal skills help bridge cultural, generational, or experiential gaps.
Interpersonal skills: Essential for teamwork and beyond
While interpersonal skills are the foundation of effective teamwork, their importance isn’t limited to collaborative settings. Interpersonal skills are just as crucial in roles that demand individual focus and independent contributions. Here’s how they apply to both:
In Teamwork:
Interpersonal skills are the lifeline of collaboration. Whether you’re brainstorming in a group, managing a team project, or resolving conflicts, these skills ensure that everyone stays aligned, motivated, and productive. For instance:
 A project manager who communicates goals clearly and encourages feedback ensures the team stays on track.
A project manager who communicates goals clearly and encourages feedback ensures the team stays on track. A team member who demonstrates empathy and adaptability can help smooth over misunderstandings, leading to better cohesion and results.
A team member who demonstrates empathy and adaptability can help smooth over misunderstandings, leading to better cohesion and results.
In Independent roles:
Even when working independently, you’re rarely in complete isolation. Strong interpersonal skills are key to interacting with clients, presenting ideas, or seeking support from colleagues. For example:
 A researcher who collaborates with stakeholders to gather insights needs active listening and clear communication.
A researcher who collaborates with stakeholders to gather insights needs active listening and clear communication. A graphic designer presenting their work to a client must empathize with their vision and provide constructive responses to feedback.
A graphic designer presenting their work to a client must empathize with their vision and provide constructive responses to feedback.
Types of Interpersonal skills and their applications
Interpersonal skills encompass a range of abilities that help individuals effectively interact and collaborate with others. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types of interpersonal skills, the sub-skills they include, and situational examples to illustrate their application:
1. Communication skills
What they are:
Communication skills involve the ability to express thoughts clearly and listen actively. This includes verbal, non-verbal, and written communication.
Skills involved:
 Active Listening
Active Listening Verbal Communication
Verbal Communication Non-verbal Communication (body language, tone)
Non-verbal Communication (body language, tone) Written Communication
Written Communication Asking Questions
Asking Questions
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Describe a time when you had to explain a complex idea to someone with less knowledge about the topic. How did you ensure they understood?”
“Describe a time when you had to explain a complex idea to someone with less knowledge about the topic. How did you ensure they understood?” “Tell me about a situation where your listening skills helped resolve a misunderstanding.”
“Tell me about a situation where your listening skills helped resolve a misunderstanding.”
Situational example:
 Scenario: During a meeting, a team member notices confusion among peers regarding a new process. They step up, use simple language, and clarify the steps, ensuring everyone is aligned.
Scenario: During a meeting, a team member notices confusion among peers regarding a new process. They step up, use simple language, and clarify the steps, ensuring everyone is aligned.
Read more: Reasons why soft skills are important for your career
2. Teamwork skills
What they are:
The ability to work collaboratively with others toward a common goal. It involves cooperation, accountability, and mutual respect.
Skills involved:
 Collaboration
Collaboration Conflict Management
Conflict Management Accountability
Accountability Trust Building
Trust Building
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Give an example of a time when you worked with someone whose working style was very different from yours. How did you handle it?”
“Give an example of a time when you worked with someone whose working style was very different from yours. How did you handle it?” “Describe a time when you went above and beyond to help your team succeed.”
“Describe a time when you went above and beyond to help your team succeed.”
Situational example:
 Scenario: A team is working on a tight deadline, and one member is falling behind. Another teammate steps in to help complete the task, ensuring the group meets its objective on time.
Scenario: A team is working on a tight deadline, and one member is falling behind. Another teammate steps in to help complete the task, ensuring the group meets its objective on time.
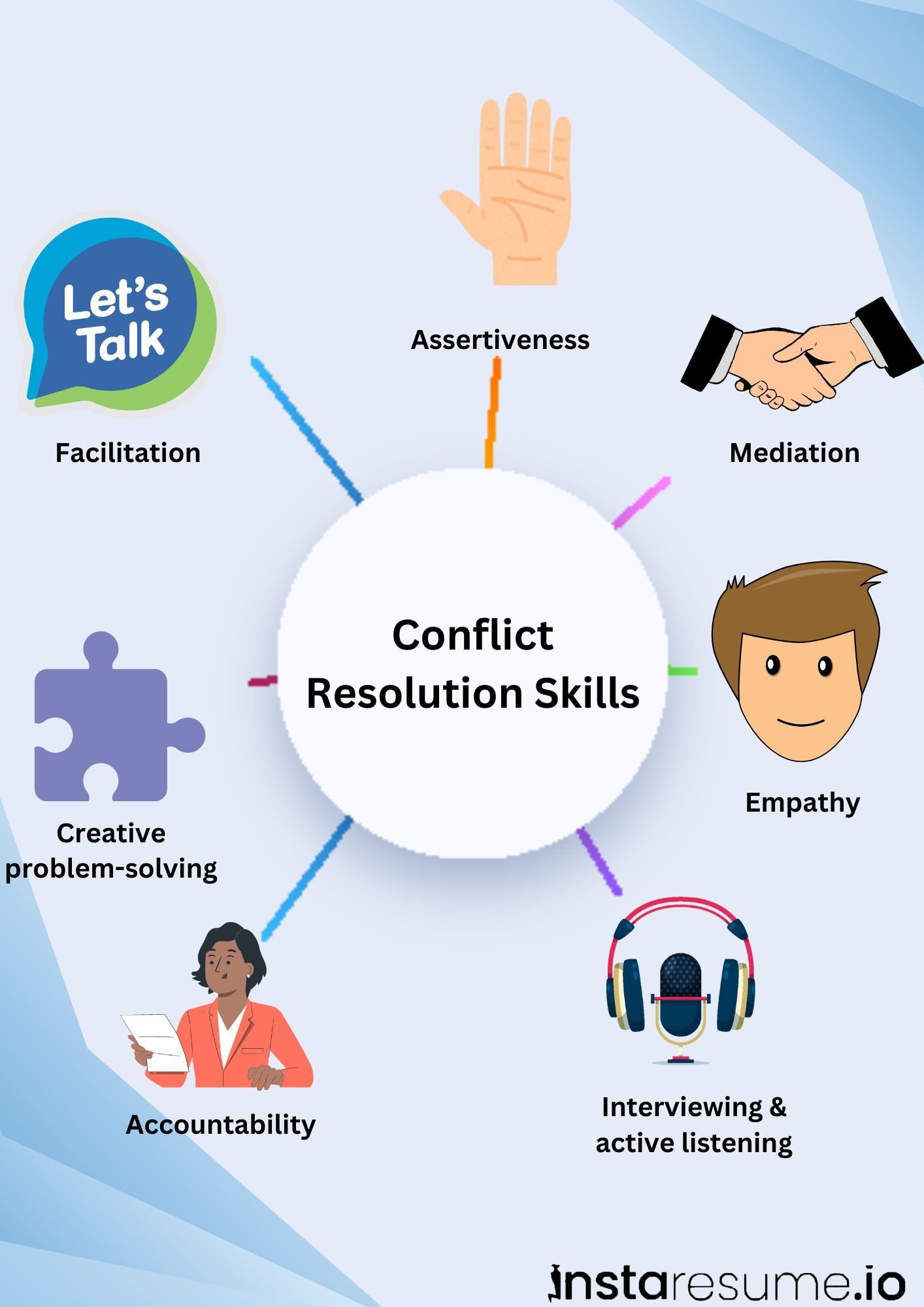
3. Conflict resolution skills
What they are:
Conflict resolution skills help in managing and resolving disputes constructively while maintaining relationships.
Skills involved:
 Negotiation
Negotiation Mediation
Mediation Problem-Solving
Problem-Solving Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Tell me about a time you resolved a conflict between two colleagues or team members.”
“Tell me about a time you resolved a conflict between two colleagues or team members.” “Describe a situation where you had a disagreement with a coworker. How did you handle it?”
“Describe a situation where you had a disagreement with a coworker. How did you handle it?”
Situational example:
 Scenario: Two team members disagree on how to approach a project. A third colleague steps in, listens to both perspectives, and proposes a solution that integrates both ideas, satisfying both parties.
Scenario: Two team members disagree on how to approach a project. A third colleague steps in, listens to both perspectives, and proposes a solution that integrates both ideas, satisfying both parties.
4. Leadership skills
What they are:
Leadership involves guiding, inspiring, and motivating others toward achieving shared goals.
Skills involved:
 Decision-Making
Decision-Making Delegation
Delegation Inspiring Others
Inspiring Others Problem-Solving
Problem-Solving
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Describe a time when you took on a leadership role during a challenging project.”
“Describe a time when you took on a leadership role during a challenging project.” “How do you motivate your team when they are struggling to meet deadlines?”
“How do you motivate your team when they are struggling to meet deadlines?”
Situational example:
 Scenario: During a project, the team faces an unexpected challenge. The leader steps in, reassesses priorities, and motivates the group to adapt and find solutions, keeping morale high.
Scenario: During a project, the team faces an unexpected challenge. The leader steps in, reassesses priorities, and motivates the group to adapt and find solutions, keeping morale high.
5. Empathy skills
What they are:
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It helps in building trust and rapport.
Skills involved:
 Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence Active Listening
Active Listening Compassion
Compassion
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Tell me about a time you recognized someone’s struggles and offered support.”
“Tell me about a time you recognized someone’s struggles and offered support.” “How do you handle feedback that involves understanding someone else’s emotions?”
“How do you handle feedback that involves understanding someone else’s emotions?”
Situational example:
 Scenario: A coworker is visibly stressed about a tight deadline. Another teammate notices and offers to help with a portion of their workload, easing their burden.
Scenario: A coworker is visibly stressed about a tight deadline. Another teammate notices and offers to help with a portion of their workload, easing their burden.
6. Adaptability skills
What they are:
Adaptability refers to one’s ability to adjust to changes and remain effective in dynamic environments.
Skills involved:
 Flexibility
Flexibility Open-Mindedness
Open-Mindedness Problem-Solving
Problem-Solving
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Describe a situation where you had to adapt quickly to a significant change at work.”
“Describe a situation where you had to adapt quickly to a significant change at work.” “How do you handle unexpected changes in priorities?”
“How do you handle unexpected changes in priorities?”
Situational example:
 Scenario: Midway through a project, a client changes the requirements. The team adjusts their strategy, reallocates resources, and successfully meets the revised objectives.
Scenario: Midway through a project, a client changes the requirements. The team adjusts their strategy, reallocates resources, and successfully meets the revised objectives.
7. Positive attitude
What they are:
A positive attitude involves optimism, enthusiasm, and resilience in the face of challenges.
Skills involved:
 Optimism
Optimism Resilience
Resilience Stress Management
Stress Management
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “Tell me about a time you stayed motivated during a challenging situation.”
“Tell me about a time you stayed motivated during a challenging situation.” “How do you keep your team’s morale up during stressful times?”
“How do you keep your team’s morale up during stressful times?”
Situational example:
 Scenario: A team faces multiple setbacks during a project. One member consistently encourages the group, helping them stay focused and motivated despite the challenges.
Scenario: A team faces multiple setbacks during a project. One member consistently encourages the group, helping them stay focused and motivated despite the challenges.
8. Time management skills
What they are:
Time management involves effectively prioritizing tasks and managing resources to meet deadlines.
Skills involved:
 Organization
Organization Prioritization
Prioritization Goal Setting
Goal Setting
Examples of behavioral questions:
 “How do you prioritize tasks when you have multiple deadlines?”
“How do you prioritize tasks when you have multiple deadlines?” “Describe a time when you had to complete a high-priority project under a tight deadline.”
“Describe a time when you had to complete a high-priority project under a tight deadline.”
Situational example:
 Scenario: A team has overlapping deadlines for two major projects. A member organizes a schedule, ensures clear task assignments, and keeps the team focused, allowing both projects to be completed on time.
Scenario: A team has overlapping deadlines for two major projects. A member organizes a schedule, ensures clear task assignments, and keeps the team focused, allowing both projects to be completed on time.
The interpersonal skills
advantage
The truth is, no matter your role, interpersonal skills are the glue that holds everything together. They’re the unsung heroes of both teamwork and individual success. Whether you're part of a cross-functional team solving complex problems or independently navigating client relationships, these skills ensure you connect meaningfully and work effectively.
And the best part is that they’re learnable. With practice, reflection, and a willingness to grow, anyone can sharpen their interpersonal skills and unlock new opportunities at work and beyond.
Examples of Interpersonal skills in action
Here are some real-world examples that highlight how interpersonal skills come into play in various scenarios:
1. Communication
Scenario: During a team meeting, a colleague explains a complex idea in simple, clear terms so everyone understands. They also actively listen to feedback and clarify doubts.
Why it matters: Good communication prevents misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page.
2. Empathy
Scenario: A manager notices an employee struggling with personal issues and offers support, adjusting deadlines to reduce stress.
Why it matters: Empathy fosters trust and builds stronger, more supportive relationships.
3. Teamwork
Scenario: During a group project, a team member collaborates effectively, respects others’ ideas, and contributes their fair share to meet the deadline.
Why it matters: Teamwork ensures goals are met efficiently while maintaining harmony in the group.
4. Conflict Resolution
Scenario: Two coworkers have a disagreement over task responsibilities. Another teammate mediates by calmly facilitating a discussion, helping them reach a compromise.
Why it matters: Resolving conflicts constructively keeps the workplace positive and productive.
5. Adaptability
Scenario: A marketing professional quickly adjusts their campaign strategy after receiving new data, working with the team to align with the revised goals.
Why it matters: Adaptability helps teams navigate unexpected changes without losing momentum.
6. Leadership
Scenario: A team leader motivates their group by clearly defining goals, recognizing achievements, and guiding them through challenges.
Why it matters: Leadership inspires collaboration and drives success.
7. Patience
Scenario: A customer service representative stays calm while addressing a frustrated client’s concerns, ensuring the issue is resolved without escalation.
Why it matters: Patience leads to better problem-solving and customer satisfaction.
8. Positive attitude
Scenario: A teammate maintains enthusiasm during a challenging project, encouraging others to stay focused and optimistic.
Why it matters: Positivity boosts team morale and keeps everyone motivated.
How to showcase your interpersonal skills during job applications and interviews
Having strong interpersonal skills is essential, but knowing how to showcase them during your job search is equally important. Not all job roles require the same set of interpersonal skills, so tailoring your approach based on the job posting is key. Here’s how you can effectively highlight your interpersonal skills from the very start:
1. Scan the job advertisement
Start by carefully analyzing the job description to identify the interpersonal skills the employer values most. Different roles demand different skills, so look for keywords that align with your strengths.
Example:
Job Ad: “Looking for a collaborative team player with excellent communication and problem-solving skills to join our fast-paced marketing team.”
 This ad prioritizes teamwork, communication, and problem-solving as key interpersonal skills.
This ad prioritizes teamwork, communication, and problem-solving as key interpersonal skills.
Once you identify the focus, tailor your resume and interview responses to highlight those specific skills.
2. Add Relevant Skills to Your Resume
Customize your resume to reflect the interpersonal skills that match the job requirements. Use action verbs and results-oriented examples to showcase your experience.
Example:
For the job above, your resume might include:
 Communication: "Led weekly cross-functional meetings, ensuring seamless collaboration and clarity across departments."
Communication: "Led weekly cross-functional meetings, ensuring seamless collaboration and clarity across departments." Teamwork: "Collaborated with a diverse marketing team to execute a campaign that increased brand engagement by 25%."
Teamwork: "Collaborated with a diverse marketing team to execute a campaign that increased brand engagement by 25%." Problem-Solving: "Identified and resolved client feedback bottlenecks, reducing response times by 15%."
Problem-Solving: "Identified and resolved client feedback bottlenecks, reducing response times by 15%."
Tip: Include a "Skills" section on your resume to list the specific interpersonal skills mentioned in the job description.
3. Demonstrate Skills in Your Cover Letter
Use your cover letter to narrate a story or example that demonstrates your interpersonal skills in action. Align your narrative with the job’s requirements.
Example:
"In my previous role as a marketing associate, I spearheaded a cross-department initiative that required constant collaboration and clear communication. By fostering open dialogue and resolving team conflicts quickly, we successfully launched a product campaign that exceeded its goals by 20%."
4. Use the STAR method in interviews
During interviews, showcase your interpersonal skills using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). This approach provides concrete examples that demonstrate your abilities.
Example behavioral question:
"Can you tell me about a time when you resolved a conflict in a team?"
Response using STAR:
 Situation: "In my last role, two teammates had conflicting ideas about how to approach a client project."
Situation: "In my last role, two teammates had conflicting ideas about how to approach a client project." Task: "As the project lead, it was my responsibility to ensure collaboration and meet the deadline."
Task: "As the project lead, it was my responsibility to ensure collaboration and meet the deadline." Action: "I facilitated a meeting where both shared their perspectives, then helped them identify common ground to combine the best elements of their ideas."
Action: "I facilitated a meeting where both shared their perspectives, then helped them identify common ground to combine the best elements of their ideas." Result: "The team delivered an innovative solution that the client praised, and it strengthened our working relationships."
Result: "The team delivered an innovative solution that the client praised, and it strengthened our working relationships."
5. Show interpersonal skills through your behavior
From the moment you interact with an employer, your interpersonal skills are on display. Here's how to make a strong impression:
 Professional Communication: Respond promptly and politely to emails. Use clear, concise language.
Professional Communication: Respond promptly and politely to emails. Use clear, concise language. Active Listening: During the interview, listen carefully to the interviewer’s questions and respond thoughtfully.
Active Listening: During the interview, listen carefully to the interviewer’s questions and respond thoughtfully. Positive Body Language: Smile, maintain eye contact, and use open gestures to convey confidence and approachability.
Positive Body Language: Smile, maintain eye contact, and use open gestures to convey confidence and approachability.
6. Tailor Skills to the Role
Here’s how to align interpersonal skills with specific roles:
 For Leadership Roles: Highlight skills like decision-making, team motivation, and conflict resolution.
For Leadership Roles: Highlight skills like decision-making, team motivation, and conflict resolution.
Example: "Led a team of 10 to complete a project 15% ahead of schedule while maintaining a 100% satisfaction rate among stakeholders." For Client-Facing Roles: Focus on communication, empathy, and relationship-building.
For Client-Facing Roles: Focus on communication, empathy, and relationship-building.
Example: "Developed long-term client relationships, increasing repeat business by 30%." For Independent Roles: Showcase adaptability and problem-solving.
For Independent Roles: Showcase adaptability and problem-solving.
Example: "Resolved unexpected challenges independently, saving the company $10,000 in project costs."
7. Ask smart questions during the interview
Demonstrate your interpersonal skills by asking thoughtful questions that show your collaborative and empathetic nature.
Example Questions:
 "How does this role collaborate with other departments?"
"How does this role collaborate with other departments?" "What’s the team dynamic like, and how can I contribute effectively?"
"What’s the team dynamic like, and how can I contribute effectively?"
8. Build your online presence
Highlight your interpersonal skills on LinkedIn or professional platforms by sharing stories, testimonials, or achievements.
 Example: Post about a time you successfully led a team or resolved a challenge, showcasing your interpersonal abilities in action.
Example: Post about a time you successfully led a team or resolved a challenge, showcasing your interpersonal abilities in action.
9. Practice, reflect, and improve
If you’re unsure how to highlight your interpersonal skills effectively, practice with a mentor, career coach, or even a friend. Ask for feedback to refine your delivery.
By tailoring your application materials, strategically demonstrating your abilities during interviews, and showing your interpersonal strengths in real-time interactions, you can capture the interviewer’s attention and stand out as the ideal candidate.
How To Improve Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are essential for building strong relationships and thriving in both personal and professional environments. Developing these skills requires self-awareness, practice, and a commitment to improving how you interact with others.
1. Practice active listening
What It Means:
Truly focus on what others are saying without interrupting, and show that you understand their perspective.
How to Develop:
 Maintain eye contact and use body language (nodding, smiling) to show engagement.
Maintain eye contact and use body language (nodding, smiling) to show engagement. Repeat or paraphrase what the other person says to confirm understanding.
Repeat or paraphrase what the other person says to confirm understanding. Avoid distractions like checking your phone during conversations.
Avoid distractions like checking your phone during conversations.
2. Improve communication skills
What It Means:
Being able to convey ideas clearly and effectively in verbal, non-verbal, and written forms.
How to Develop:
 Work on public speaking by joining a group like Toastmasters or practicing with friends.
Work on public speaking by joining a group like Toastmasters or practicing with friends. Simplify your language to ensure clarity when explaining complex ideas.
Simplify your language to ensure clarity when explaining complex ideas. Be mindful of your tone and body language, as they can reinforce or contradict your words.
Be mindful of your tone and body language, as they can reinforce or contradict your words.
3. Build empathy
What It Means:
Understanding and sharing the feelings of others to build trust and connection.
How to Develop:
 Actively try to see situations from others’ perspectives.
Actively try to see situations from others’ perspectives. Ask open-ended questions to understand their thoughts and emotions better.
Ask open-ended questions to understand their thoughts and emotions better. Be patient and avoid judgment when someone shares their experiences.
Be patient and avoid judgment when someone shares their experiences.
4. Foster teamwork
What It Means:
Collaborating effectively with others to achieve shared goals.
How to Develop:
 Volunteer for group projects and practice being both a leader and a contributor.
Volunteer for group projects and practice being both a leader and a contributor. Learn to delegate tasks and recognize the strengths of others in the team.
Learn to delegate tasks and recognize the strengths of others in the team. Celebrate team successes and give credit where it’s due.
Celebrate team successes and give credit where it’s due.
5. Strengthen conflict resolution skills
What It Means:
Resolving disagreements constructively while maintaining positive relationships.
How to Develop:
 Stay calm and focus on the issue, not the individual.
Stay calm and focus on the issue, not the individual. Practice active listening to understand all perspectives in a disagreement.
Practice active listening to understand all perspectives in a disagreement. Propose solutions that consider everyone’s needs and find a middle ground.
Propose solutions that consider everyone’s needs and find a middle ground.
6. Develop adaptability
What It Means:
Adjusting your behavior and approach in response to changing circumstances.
How to Develop:
 Embrace feedback and use it to improve.
Embrace feedback and use it to improve. Seek out new challenges that push you out of your comfort zone.
Seek out new challenges that push you out of your comfort zone. Practice staying positive and proactive when plans change unexpectedly.
Practice staying positive and proactive when plans change unexpectedly.
7. Cultivate a positive attitude
What It Means:
Displaying optimism and enthusiasm even in challenging situations.
How to Develop:
 Practice gratitude by acknowledging the positive aspects of your day.
Practice gratitude by acknowledging the positive aspects of your day. Focus on solutions instead of dwelling on problems.
Focus on solutions instead of dwelling on problems. Surround yourself with positive influences to reinforce your mindset.
Surround yourself with positive influences to reinforce your mindset.
8. Enhance emotional intelligence (EQ)
What It Means:
Recognizing, understanding, and managing your emotions and those of others.
How to Develop:
 Reflect on your emotions during interactions and how they affect others.
Reflect on your emotions during interactions and how they affect others. Learn to control impulsive reactions in tense situations.
Learn to control impulsive reactions in tense situations. Use feedback from others to identify areas for improvement.
Use feedback from others to identify areas for improvement.
9. Seek feedback
What It Means:
Learning about your interpersonal strengths and areas for growth through others’ perspectives.
How to Develop:
 Ask trusted colleagues, friends, or mentors for honest feedback on your interactions.
Ask trusted colleagues, friends, or mentors for honest feedback on your interactions. Be open to constructive criticism without becoming defensive.
Be open to constructive criticism without becoming defensive. Use feedback to set specific goals for improvement.
Use feedback to set specific goals for improvement.
10. Practice self-awareness
What It Means:
Understanding how your actions and emotions affect others.
How to Develop:
 Reflect on your daily interactions and identify areas where you could improve.
Reflect on your daily interactions and identify areas where you could improve. Keep a journal to track situations where you struggled or excelled in interpersonal communication.
Keep a journal to track situations where you struggled or excelled in interpersonal communication. Regularly assess your progress in building stronger relationships.
Regularly assess your progress in building stronger relationships.
11. Build relationships outside your comfort zone
What It Means:
Interacting with people from different backgrounds or perspectives to broaden your understanding.
How to Develop:
 Join clubs, volunteer groups, or professional associations.
Join clubs, volunteer groups, or professional associations. Engage in conversations with colleagues or peers you don’t usually interact with.
Engage in conversations with colleagues or peers you don’t usually interact with. Be curious and respectful about cultural and personal differences.
Be curious and respectful about cultural and personal differences.
12. Learn conflict mediation
What It Means:
Helping others resolve disputes in a fair and constructive manner.
How to Develop:
 Take courses or read books on conflict resolution techniques.
Take courses or read books on conflict resolution techniques. Act as a mediator in small disagreements among friends or colleagues.
Act as a mediator in small disagreements among friends or colleagues. Practice staying neutral and focused on solutions.
Practice staying neutral and focused on solutions.
13. Attend workshops or training programs
What It Means:
Investing in professional development to improve interpersonal skills.
How to Develop:
 Enroll in courses on communication, emotional intelligence, or leadership.
Enroll in courses on communication, emotional intelligence, or leadership. Participate in role-playing exercises to practice scenarios.
Participate in role-playing exercises to practice scenarios. Use online platforms like LinkedIn Learning or Coursera for structured learning.
Use online platforms like LinkedIn Learning or Coursera for structured learning.
FAQs for interpersonal skills
What is interpersonal skills training?
Interpersonal skills training is a structured program that helps individuals improve communication, teamwork, and relationship-building abilities in personal and professional settings. Many organizations invest in such training to enhance employee collaboration and workplace efficiency.
How do interpersonal skills courses online help professionals?
Online interpersonal skills courses provide flexibility for professionals to learn at their own pace. They often cover modules on conflict resolution, active listening, leadership communication, and workplace collaboration—making them valuable for career growth.
Why is business communication and interpersonal skills important in the workplace?
Business communication and interpersonal skills are crucial because they directly impact productivity, teamwork, and leadership effectiveness. Employees with strong communication skills reduce misunderstandings and contribute to a positive organizational culture.
What are soft skills training programs for professionals?
Soft skills training programs focus on improving interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, and adaptability. These programs are highly valued by employers in the USA who want employees with both technical and people-centric skills.
How do leadership and interpersonal communication workshops work?
Leadership and interpersonal communication workshops combine theory with practical activities such as role-plays, case studies, and group discussions. They prepare leaders to handle conflicts, motivate teams, and drive organizational success.
What is communication skills coaching, and who needs it?
Communication skills coaching is one-on-one or group guidance aimed at helping individuals improve public speaking, negotiation, and interpersonal communication. Executives, managers, and job seekers often seek coaching to gain a competitive edge.
Why is effective communication training essential in the workplace?
Effective communication training teaches employees how to express ideas clearly, listen actively, and collaborate effectively. In the U.S., many companies prioritize such training because it boosts efficiency, customer satisfaction, and employee retention.
What are assertiveness and interpersonal skills seminars?
Assertiveness and interpersonal skills seminars teach professionals how to express themselves confidently while respecting others. These seminars are popular in corporate environments where clear, respectful communication is critical.
How valuable are interpersonal skills certification programs?
Certification programs validate an individual’s proficiency in interpersonal and communication skills. For U.S. professionals, such certifications can improve job prospects, strengthen resumes, and demonstrate commitment to personal growth.
How does emotional intelligence training improve interpersonal relationships?
Emotional intelligence training enhances self-awareness, empathy, and conflict management. By improving emotional intelligence, individuals strengthen interpersonal relationships, build trust, and create a healthier workplace environment.
Over time, these habits strengthen interpersonal communication skills and help you build better professional and personal relationships. Whether you’re in a job interview, team meeting, or client call, strong interpersonal skills improve trust, collaboration, and overall success.